© Sebastian Kaulitzki – stock.adobe.com
News • Voice box cancer treatment
Laryngeal cancer: AI software to better predict outcomes
Artificial intelligence has been found to improve the outcome of patients with voice box cancer, which is a step closer to personalised treatment, new research has revealed.
In the first-of-its-kind research into advanced laryngeal cancer (or voice box cancer), Mr Amar Rajgor and his team at Newcastle University have tapped into the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to analyse medical imaging from CT scans, which is aimed at predicting survival. The research was published in the Journal of Laryngology & Otology.
Laryngeal cancer is a tough battle for many in the UK, with around 2,400 new cases diagnosed each year, with half of those in advanced stages not surviving beyond three years. However, this study, led by Mr Rajgor, offers hope for improved care and treatment for patients.
Currently, much of the information from scans is not being fully utilized, but this allows us to unlock its full potential
Amar Rajgor
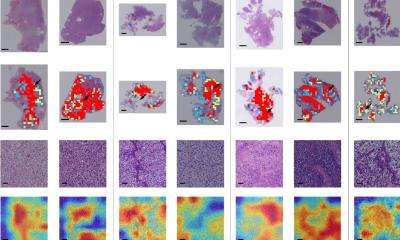
The AI software operates pixel by pixel, revealing hidden patterns within the tumour that cannot be seen by the human eye. This can act as a “virtual biopsy” and provide clues regarding the cancer’s behaviour and the extent of irregularity. This new way of looking at images in such detail, is called radiomics.
Speaking on his findings, Mr Rajgor, an ear, nose and throat specialist, said: “Radiomics can be seen as a super-powered magnifying glass for medical images, like CT scans. It carefully examines every tiny detail, even the ones that are hard to see. By doing this, it can find patterns and irregularities that cannot be seen by a human or might otherwise be missed.”
The research revealed two important imaging markers, Shape Compactness and Grey Level Non-Uniformity (GLNU). If these markers are high, it indicates a patient has a greater chance of dying sooner. An increase in Shape Compactness amplified the risk of death nearly threefold, while a rise in GLNU doubled the risk. The results also revealed that these imaging markers did a better job at predicting survival compared to the traditional factors doctors currently use, like age or stage of cancer.
There are a number of studies done that analyse all head and neck cancers, however, those studies are not robust or clinically relevant as all head and neck cancer behave very differently, and from a clinicians perspective, should not be merged into one group for analysis.
Mr Rajgor added: "These developments are very exciting, as this research could play a big role in guiding treatment and delivering precision medicine in the future. It could also ensure that patients get the right treatment for them, based on what their tumour looks like and how it behaves. I hope this will also help patients make more informed decisions about their treatment journey. Another benefit is that this method does not change the patient pathway but enhances it, by analysing medical images in a way that cannot be done by a human. Currently, much of the information from scans is not being fully utilized, but this allows us to unlock its full potential. In the future, we could also use this technique to track how well a patient is responding to treatment by looking at scans over time.”
Recommended article
News • CT & ultrasound fusion
‘Virtual biopsies’ could replace tissue biopsies in the future
A new advanced computing technique using routine medical scans to enable doctors to take fewer, more accurate tumour biopsies, has been developed by cancer researchers at the University of Cambridge. This is an important step towards precision tissue sampling for cancer patients to help select the best treatment. In future the technique could even replace clinical biopsies with ‘virtual…
In the past 30 years, little progress has been made in improving survival rates for patients with voice box cancer. However, the partnership between Newcastle University and Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust offers hope for those battling laryngeal cancer. This collaboration has led to Amar Rajgor receiving a prestigious National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Doctoral Fellowship.
Mr Rajgor concluded: "Further research will be done in this area. Following my award from NIHR, we are currently expanding the study to over 250 patients. We will aim to create a risk prediction model looking at both survival and response to specific cancer treatments. This prototype model will include clinical factors, pathology detail and imaging markers. This has the potential to truly revolutionise voice box cancer management.”
Amar Rajgor's systematic review emphasizes the pitfalls of the current literature, and these have been accounted for in this study.
Source: Newcastle University
16.04.2024